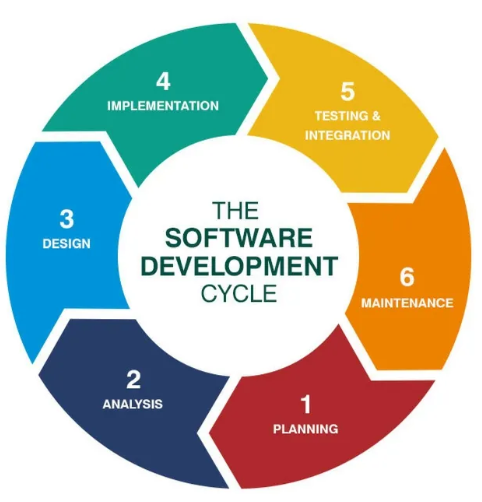
The development lifecycle, often referred to as the software development lifecycle (SDLC), is a structured and systematic process that guides the creation and evolution of software applications. It encompasses a series of phases, activities, and milestones to ensure that software is designed, developed, tested, and deployed efficiently and effectively. Here's a description of the typical software development lifecycle:
-
Planning and Requirements Gathering: This initial phase involves understanding the project's objectives, defining requirements, and determining the scope of the software. Stakeholders, including clients and end-users, provide input to create a comprehensive project plan.
-
Analysis: During this phase, the project team analyzes the gathered requirements, assesses technical feasibility, and identifies potential risks. The goal is to establish a clear understanding of what the software needs to achieve.
-
Design: In the design phase, architects and developers create the system's architecture, technical specifications, and user interface. They outline the software's structure, components, and how it will meet the specified requirements.
-
Development: The actual coding and programming of the software occur in this phase. Developers write and test the source code, following the design specifications. This phase also includes code reviews and quality assurance.
-
Testing: Once development is complete, the software undergoes rigorous testing. This includes unit testing, integration testing, and system testing to identify and fix any defects or issues.
-
Maintenance: This section is covered below under DevOps.
The specific software development lifecycle mode used at Youtap is a mixture of Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, and DevOps. Ultimately, the development lifecycle provides a framework to guide software projects from inception to successful implementation and beyond.
In the design phase, architects and developers create the system's architecture, technical specifications, and user interface. They outline the software's structure, components, and how it will meet the specified requirements.
DevOps
The Youtap DevOps lifecycle is a series of interconnected stages and activities that guide the development and deployment of software applications, emphasizing collaboration and automation to achieve more efficient and reliable results. The DevOps lifecycle typically consists of the following phases:
The DevOps lifecycle is characterized by iterative, continuous improvement. Feedback loops and automation play a crucial role in each phase, ensuring that software development and deployment processes are streamlined, efficient, and reliable. By fostering collaboration and automation, DevOps helps organizations deliver high-quality software more rapidly, adapt to changes, and respond to user needs and market demands effectively.
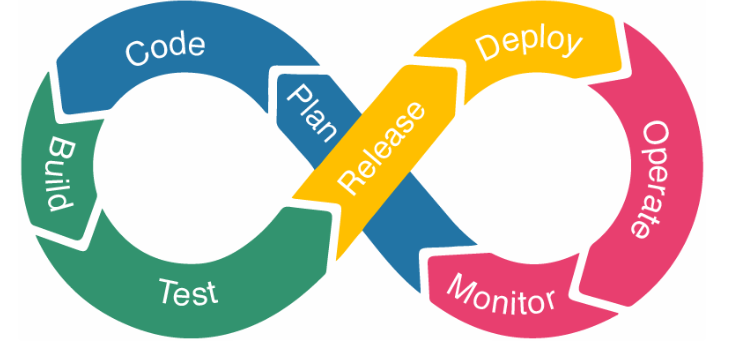
Plan, Code, Build and Test are covered as part of the SDLC, the second part of this loop focuses on deploy and updating production.
-
Deployment: After successful testing and approval, the software is deployed to production environments. Deployment activities include configuring servers, databases, and network settings, as well as ensuring compatibility with the target infrastructure.
-
Operation and Maintenance: The software is now in active use, and this phase involves monitoring its performance, addressing any operational issues, and applying updates and patches as necessary. User feedback is crucial for making improvements.
-
Monitoring and Optimization: Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure that the software performs well and remains secure. Data is collected to identify areas for optimization, enhancements, and scaling to accommodate growth or changes in user needs.
-
Documentation: Throughout the development lifecycle, documentation is created and maintained to explain the software's architecture, usage, and maintenance requirements. This documentation aids in training and future development efforts.
-
End of Life (EOL) or Retirement: When the software reaches the end of its useful life, it is either replaced or retired. This phase involves data migration, archiving, and ensuring a smooth transition to a new system if necessary.
