Testing and Quality Assurance are crucial components of the Software Development Lifecycle that ensure the software being developed meets quality standards and functions as intended.
Here's an overview of the processes involved:
Test Planning (PLAN)
-
Requirement Analysis: The QA team begins by thoroughly understanding the project's requirements, including functional and non-functional requirements, that are documented in Confluence.
-
Test Strategy: A test strategy is developed to outline the overall approach to testing, including the scope, objectives, resources, and timelines. Example of template is Test Strategy & Plan - Template
-
Test Plan: A detailed test plan is created, specifying the testing phases, test environments, test data, entry/exit criteria, and responsibilities. This plan serves as a roadmap for testing activities.
Test Case Creation and Management (DEVELOP)
-
Test Case Design: QA engineers design test cases based on the requirements and test plan. Test cases include inputs, expected outputs, and actions to perform.
-
Test Case Management: All the test-cases are documented in Test case management tool (Testrail) for traceability and test matrix.
-
Test Data Preparation: As required for the test-cases, Test-data needs to be prepared up-front, ready for test execution.
-
Create realistic test data
-
Test Execution (TEST)
-
Test Execution: QA engineers execute test cases and perform all types of tests that are in-scope, following the test plan.
-
Get/Confirm the release version/build that are Ready to Test
-
Every execution need to create the test run, and if in 1 cycle consist of more than 1 test run and then you need to create a Milestone
-
Test execution can result to QA Passed status or QA Blocked status or QA Failed status (and may result the creation of bug ticket)
-
All test cases executed, the test-results are documented and testrail link put in Jira.
-
Some testing activity need to check the system logs.
-
Some good practice of ways of working Ways of Working - QA Engineer
-
-
Regression Testing: After each code change or build, regression tests are executed to ensure that new updates haven't introduced new defects nor affected existing functionality.
-
Exploratory Testing: QA engineers may also perform exploratory testing to uncover unexpected issues.
-
Non Functional Testing: Any NFT (Non-Functional Testing) is complete, if applicable.
-
Automation test planning is a must. Automation Testing - Dashboard
-
Defect Reporting and re-testing
-
Defect Identification: When a test case fails, QA engineers identify and document defects, including all necessary details as steps to reproduce, env, screenshots/ logs/ videos to aid debugging. Put the Jira ticket numbers on Testrail.
-
Defect Verification: After developers fix a defect, QA engineers verify the fix by retesting the affected test case; Also, perform Regression tests to ensure that the code change hasn’t introduced any new defects. You can plan the regression cycle within your sprint schedule.
RELEASE
-
Test (Summary) Report: Test Run Report / Test Milestone Report (Compilation of Test Run), Consist of Scope of Testing (i.e. release note), what cannot be tested, and the evidence of the report
-
Smoke Test: To make sure we have the correct build and work as expected
-
Prepare the Smoke Test Plan in advance and have been agree and/or acknowledge by the stake holder
-
Dev/Release production build that able to test
-
-
BAST: Berita Acara Testing
-
Follow-Up & Return to Normal Plan (if any): Clean the test data
The Role of QA in the SDLC
The role of QA is critical in the SDLC to ensure the delivery of high-quality software. Here's how QA fits into the various phases of the SDLC:
-
Requirements Walk-thru: QA professionals participate in understanding the requirements, to ensure that requirements (both functional and non-functional) are clear, complete, and testable.
-
Development Phase: While developers code, QA start preparing test cases and test data for upcoming testing phases. In addition, automation test script and load test if possible.
-
Testing Phase: QA is heavily involved in test planning, test case creation, and execution. They validate that the software meets requirements and is mostly free of defects. During the testing QA also need to check the log while testing.
-
Deployment Phase: QA verifies that the software is ready for deployment, ensuring that all the agreed exit criteria have been satisfied. Including the smoke test coverage.
Example of Definition of Done (DoD)
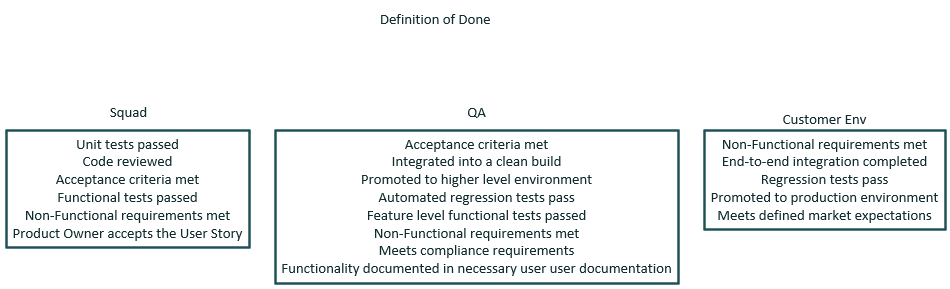
No Critical Defects
-
There are no high-priority defects left-out during testing. Any minor defects are documented in the backlog.
